Nephrotic Syndrome
Clinical manifestations associated with the loss of negative charge on the glomerular basement membrane. This allows albumin to escape from the arterioles into the glomerular capsule, resulting in proteinuria.
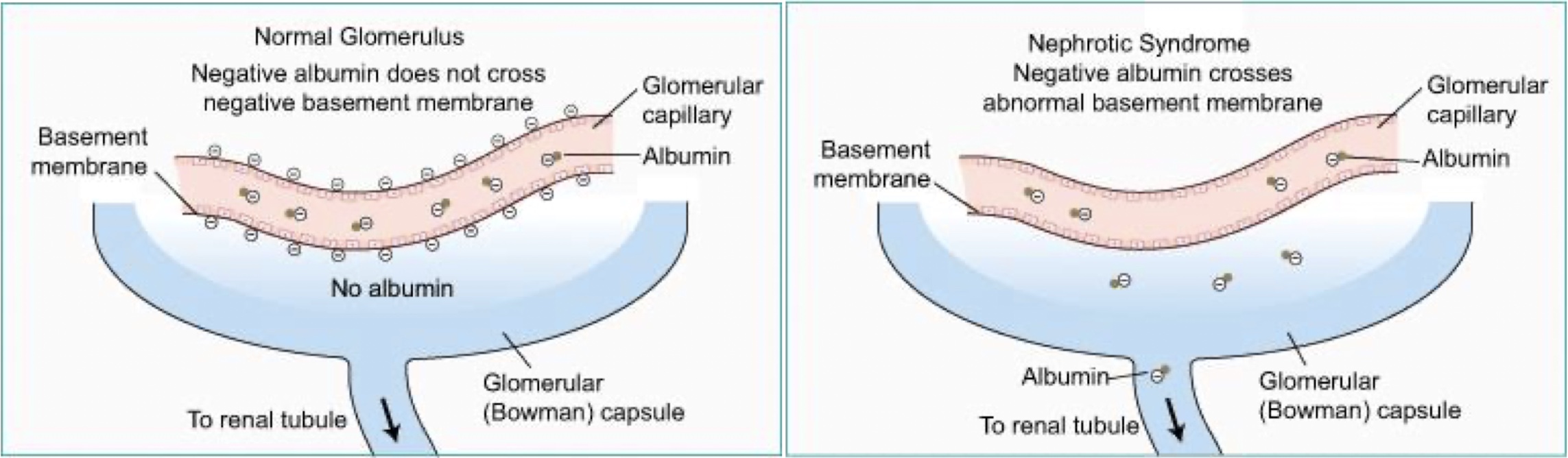
Effects of nephrotic syndrome:
- Proteinuria of 3.0 to 3.5 g/day.
- Proteinuria leads to hypoalbuminemia and decreased blood osmotic pressure, resulting in...
- Hyperlipidemia and hypercoagulability as liver attempts to replace albumin.
Management of nephrotic syndrome includes the following, until the underlying cause is discovered.
- Diuretics.
- Lipid-lowering agents.
- Anti-hypertensives.
- Immunosuppression.
Nephrotic syndrome may resolve spontaneously or may progress to end-stage renal disease.